The Dangers of Kidney Cancer and How to Prevent It
Understanding Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cancer, originates in the kidneys, which are two bean-shaped organs located behind the abdominal organs. The most common type of kidney cancer in adults is renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Early detection is crucial as kidney cancer often doesn’t cause symptoms until it has advanced.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing kidney cancer:
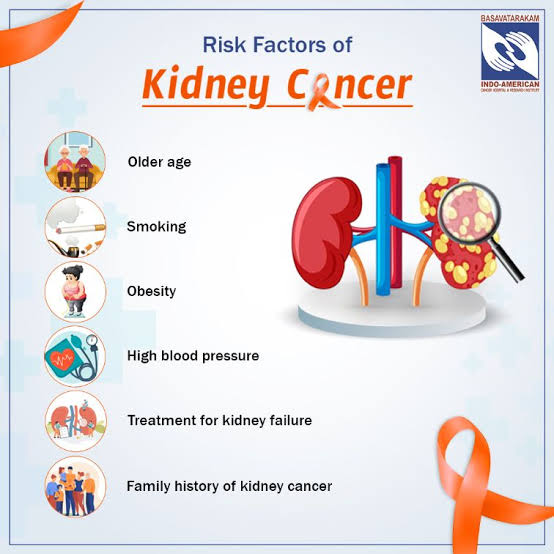
Smoking: Increases the risk of RCC, with the risk decreasing gradually after quitting.
Obesity: Excess body weight can lead to hormonal changes that increase the risk.
High Blood Pressure: Hypertension is a significant risk factor.
Family History: A strong family history of RCC can elevate risk.
Chemical Exposure: Workplace exposure to certain chemicals like trichloroethylene.
Gender: Men are more likely to develop kidney cancer than women.
Age: The risk increases with age.
Symptoms
Kidney cancer often doesn’t show symptoms in its early stages. When symptoms do appear, they may include.
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
Persistent pain in the side or back
Loss of appetite
Unexplained weight loss
Fatigue
Prevention Strategies
While not all cases of kidney cancer can be prevented, certain lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk:
Quit Smoking: Avoiding tobacco is one of the most effective ways to lower the risk.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Aim for a body mass index (BMI) below 25.
Healthy Diet: Eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables and low in processed foods.
Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activity daily.
Control Blood Pressure: Keep your blood pressure in check through diet, exercise, and medication if necessary.
Avoid Chemical Exposure: Be cautious with chemicals, especially in the workplace.
Conclusion
Kidney cancer poses significant health risks, but many of these risks can be mitigated through lifestyle changes and regular medical check-ups. By understanding the risk factors and adopting preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their chances of developing this serious condition.
For more detailed information, consult healthcare professionals and trusted medical resources.










